3D Printing Machines / 3D Printers
- The wall printer machine can automatically directly printing any images on wall and any vertical surfaces with real 3D effect.
- Materialise software is built on more than 25 years of experience and open collaboration. We offer the 3D printing solutions for all businesses and industries.
Manufacturers that make the switch can leverage 3D printing software to prototype and produce parts in a single day, for a fraction of the cost of traditional CNC machining. However, there are still several key.
Used RP Machines
AT 3D-SQUARED offers a consultancy service, whereby it is able to buy used RP machines, to order, on behalf of its clients. Beyond the purchase transaction however, AT 3D-SQUARED can also upgrade/improve the functionality of the machines that they buy. In real terms this means significant improvements in the build styles of the machines and the machines throughout capabilities.
Leasing
As an alternative to the purchasing of capital equipment, the consultants of AT 3D-SQUARED are able to advise clients on the potential advantages of leasing an SLA machine.
NEW for 2015! @3D's Repair Service
We are now offering a new Repair Service for 3D Systems SLA250™ Machines
Powered by Materialise Build Processor & Machine Control Software, our Repair Service will take your existing technology and give it a second life.
After @3D's Repair Service, your Stereolithography machine will reintegrate easily into your current production environment and will:
* Be fully configurable, as well as faster, more accurate, easier to run and maintain
* Offer complete freedom in resin choice
* Provide High Resolution and High Speed modes
* Offer High Res and Normal Res on the same build
With real-time monitoring and automatic build preparation, your repaired machine will enable you to manage and optimize your 3D Printing process to its full potential.
SLA250² Specifications
Repair based on a 3DSystems SLA250™
| Laser | 355nm - 300mW | |
|---|---|---|
| Resolution | down to 0.075mm on standard hardware | |
| Spot Size | 0.06 > 1mm | |
| Material | Open to use ANY SL material | |
| Software | @3D Build Processor SL250² Machine Control Software | |
| Network | Ethernet 10/100 | |
| Power | 100-240 VAC, 50/60Hz, 900W | |
| Temp Range | 18 > 28ºC | |
| Noise (estimated) | 0dB | |
| Crated | Size: 152 x 102 x 195cm | Weight: 466Kg |
| Un-Crated | Size: 126 x 70 x 172cm | Weight: 329Kg |
Now available for the SLA500/5000 & 7000™ Any questions then please contact us or telephone: +44 (0) 7789 713087
Fore more information about these options for in-house RP facilities, contact us.
A good G-Code simulator can make the difference between a successful manufacturing process or an expensive failure. Here are some of the best simulators.
Debugging is a vital part of any programming task. This is certainly true with programs that will interact with the physical world like those used to control CNC machines, 3D printers, and robotics.
Any mistake in the programming of these physical machines could cause real damage to the environment, the machine itself, and even to human workers in the case of some robots.
G-Code simulation is probably the best way to ensure that you have written your program to a high standard. Although very few people these days write G-Code by hand — we tend to use CAM programs — there is still a huge benefit to checking your program in a simulator before loading it into your physical machine.
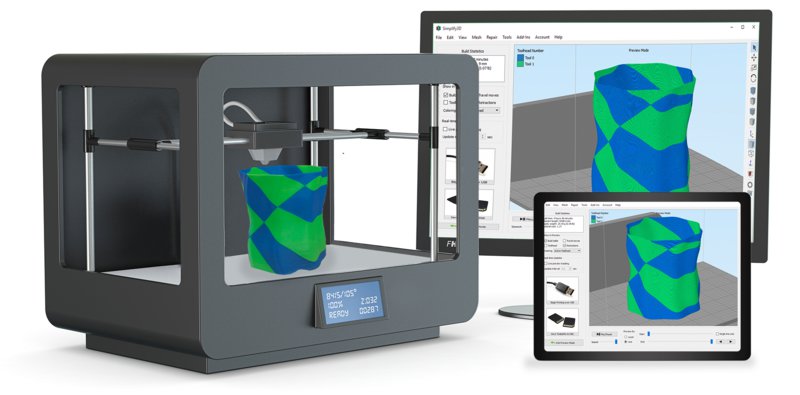
Here is a list of some of the best types of G-Code simulator that you can use these days.
What is a G-Code Simulator?
A G-Code simulator is a type of software tool that provides a virtual representation of a CNC machine's tool path made by following the instructions in a G-Code file. They range from simple simulators that output a single image of the tool path to complex tools that can detect collisions and plot the path in 3D.
The basic purpose of a G-Code simulator is to give you a way to see how the machine tool will move. Without this, the only way to debug your program is to test it out on the machine itself… and by then it's too late to avoid disaster.
G-Code simulators have experienced a resurgence in popularity over recent years thanks to the rise of 3D printing. Hobbyists and professionals alike need a way to see a 3D printed item before they spend hours printing it. A good simulator provides a quick and easy way to achieve this.
The 5 Best G-Code Simulators for Machining and 3D Printing
There are quite a few options for simulating your G-Code out there. Some of them are okay, others are a waste of time.
Here are 5 types of G-Code simulator that are all good in some situations. Which you pick depends on your unique needs for this machining or 3D printing application:
1. Stand-alone G-Code Simulator
There are some simple software tools available that will quickly simulate your G-Code file and show you the path. In general, they don't interface with CNC machines or 3D printers, but they at least give you the confidence that your program 'draws the shapes' that it's supposed to.
Some notable examples include:
- NC Viewer a handy online tool for quick visualization.
- CAMotics an open-source simulator for 3-axis machining.
- G-Code Q'n'dirty another open-source web tool.
2. Slicer Software (for 3D printing)
If you are using G-Code to program a 3D printer, your Slicer software may be able to give you a visualization of what the final printed item will look like.
A Slicer is a software tool that turns your CAD model into G-Code.
For example, RoboDK users often use the free tool Slic3er when they are using robotic 3D printing. This tool allows them to visualize the item that they are going to print before they send it to the robot.
Slic3r can also perform some of the functions of a dedicated G-Code simulator, such as estimating the time it will take to print the object and repairing incomplete 3D files.
3. RoboDK for Robotic Machining and 3D Printing
3d Printing Machine And Software
If you are considering using a robot for your machining or 3D printing, probably the best option is RoboDK (of course, we would say that, wouldn't we?… but it's also true).
RoboDK's machining and printing wizard works with G-Code.
You can load a G-Code file into the software then easily simulate the path. Then, with the same software, you can send the program directly to the robot's controller, without having to do any robot programming at all!
Not familiar with robotic machining? Check out our introductory post.
Didn't know robots could do 3D printing? Here's a video:
4. Libraries (e.g. MATLAB or Python)
There are some situations where you might want to perform some more advanced analysis on your G-Code or link with your own programming. Perhaps you are using the code as part of a research project or you are developing your own 3D printer.
In such cases, it could be helpful to use a G-Code library for your preferred programming language.
Best 3d Printing Machine
For example:
- G-Code Reader is an extension for MATLAB.
- PyCNC is a library for Python.
- Gsim is an open-source 2D simulator written in Python.

Here is a list of some of the best types of G-Code simulator that you can use these days.
What is a G-Code Simulator?
A G-Code simulator is a type of software tool that provides a virtual representation of a CNC machine's tool path made by following the instructions in a G-Code file. They range from simple simulators that output a single image of the tool path to complex tools that can detect collisions and plot the path in 3D.
The basic purpose of a G-Code simulator is to give you a way to see how the machine tool will move. Without this, the only way to debug your program is to test it out on the machine itself… and by then it's too late to avoid disaster.
G-Code simulators have experienced a resurgence in popularity over recent years thanks to the rise of 3D printing. Hobbyists and professionals alike need a way to see a 3D printed item before they spend hours printing it. A good simulator provides a quick and easy way to achieve this.
The 5 Best G-Code Simulators for Machining and 3D Printing
There are quite a few options for simulating your G-Code out there. Some of them are okay, others are a waste of time.
Here are 5 types of G-Code simulator that are all good in some situations. Which you pick depends on your unique needs for this machining or 3D printing application:
1. Stand-alone G-Code Simulator
There are some simple software tools available that will quickly simulate your G-Code file and show you the path. In general, they don't interface with CNC machines or 3D printers, but they at least give you the confidence that your program 'draws the shapes' that it's supposed to.
Some notable examples include:
- NC Viewer a handy online tool for quick visualization.
- CAMotics an open-source simulator for 3-axis machining.
- G-Code Q'n'dirty another open-source web tool.
2. Slicer Software (for 3D printing)
If you are using G-Code to program a 3D printer, your Slicer software may be able to give you a visualization of what the final printed item will look like.
A Slicer is a software tool that turns your CAD model into G-Code.
For example, RoboDK users often use the free tool Slic3er when they are using robotic 3D printing. This tool allows them to visualize the item that they are going to print before they send it to the robot.
Slic3r can also perform some of the functions of a dedicated G-Code simulator, such as estimating the time it will take to print the object and repairing incomplete 3D files.
3. RoboDK for Robotic Machining and 3D Printing
3d Printing Machine And Software
If you are considering using a robot for your machining or 3D printing, probably the best option is RoboDK (of course, we would say that, wouldn't we?… but it's also true).
RoboDK's machining and printing wizard works with G-Code.
You can load a G-Code file into the software then easily simulate the path. Then, with the same software, you can send the program directly to the robot's controller, without having to do any robot programming at all!
Not familiar with robotic machining? Check out our introductory post.
Didn't know robots could do 3D printing? Here's a video:
4. Libraries (e.g. MATLAB or Python)
There are some situations where you might want to perform some more advanced analysis on your G-Code or link with your own programming. Perhaps you are using the code as part of a research project or you are developing your own 3D printer.
In such cases, it could be helpful to use a G-Code library for your preferred programming language.
Best 3d Printing Machine
For example:
- G-Code Reader is an extension for MATLAB.
- PyCNC is a library for Python.
- Gsim is an open-source 2D simulator written in Python.
5. Your Favorite CAM Package
Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) programs are how many of us generate our G-Code files in the first place.
Popular CAM packages (which also include plugins for RoboDK) include:
Many of the leading CAM packages also have the capacity to simulate your G-Code. Often, if you want to link the software directly with your CNC machine or 3D printer, it will require you to purchase an extra add-on license, so weigh up the pros and cons beforehand. However, simple simulation can usually be achieved within the CAM software itself.
How to Pick the Best Software for You
There are clearly several ways to simulate G-Code!
But, which is going to be the best software for you? The answer depends on your situation.
If you are a hobbyist who is just using G-Code to program your home 3D printer, for example, one of the open-source, stand-alone simulators or Slicer software will probably be the best option.
If you are a researcher or programmer looking to delve deep into the simulation, one of the MATLAB or Python libraries might be worth checking out.
Finally, if you are working in industry, however, you will want a piece of software that is easy to use, robust and won't give you any unnecessary headaches. For robotic machining or 3D printing, RoboDK is a good option. For all other CNC, look at a decent CAM package.
What questions do you have about G-Code simulation? Tell us in the comments below or join the discussion on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook,Instagram or in the RoboDK Forum.
